Space Lattice – Geology Notes – For W.B.C.S. Examination.
স্পেস ল্যাটিস – ভূতত্ব নোট – WBCS পরীক্ষা।
According to Hauy (1784) a crystal is built up by a number of small crystals having the shape of the original crystal as a whole. This led to the concept of space lattice or crystal lattice.Continue Reading Space Lattice – Geology Notes – For W.B.C.S. Examination.
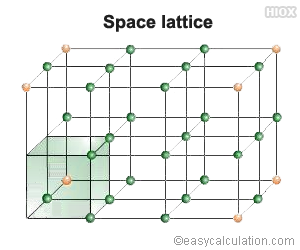
“A space lattice is an array of points showing how particles (atoms, ions or molecules) are arranged at different sites in three dimensional spaces.”
A crystal is a three dimensional design in which identical points form a 3-dimensional network of cells each representing the unit and through which whole crystal can be built up. The lattice points can be connected by a regular network of lines in various ways. Thus the lattice is broken up into a number of unit cells.
The unit cell may be defined as, “the smallest repeating unit in space lattice which, when repeated over again, results in a crystal of the given substance”.
Therefore space lattice of a crystal has been likened to a wall-paper on which a single pattern is continuously repeated. Each unit cell requires two vectors a and b for its description. A three dimensional space lattice can be similarly divided into unit cells described by three vectors. The exact location of particles in a unit cell can be obtained by X-ray diffraction.
It should be understood that the choice of unit cell is by no means unique. There are various ways in which a cell can be drawn in a unique space lattice. However, it is usually convenient to choose a parallelopipe whose edges are parallel with the crystallographic axes (a, b and c) and with the
shortest possible sides. This is termed as primitive cell. One lattice point is associated with each primitive cell.A crystalline solid has a very special structure, that gives it the unique properties of a solid. This structure is made up of repeating units which we call a unit cell.
Crystals have a structure made up of a regular arrangement of their atoms (or particles). When such an arrangement of atoms is represented in a three-dimensional structure, this is a crystal lattice. So a lattice is an array of points in a particular order which describes the arrangement of particles of a crystalline solid.
Now Auguste Bravais was French scientist who found out that there are a total of fourteen possible three-dimensional lattices. These 14 arrangements are the Bravais Lattice. They have six basic shapes. The following diagram shows you the fourteen arrangements.
Characteristics of Crystal Lattice
The fourteen Bravais Lattices show some similar characteristics. These are
- Each point on the lattice represents one particle of the crystal, This is a lattice point.
- This particular particle may be an atom, a molecule or even ions
- These lattice points of a crystal are joined together by straight lines.
- By joining of these points we get the geometry (or shape) of the crystal
- Every one of the fourteen lattices has such a unique geometry
Unit Cell
A unit cell is the most basic and least volume consuming repeating structure of any solid. It is used to visually simplify the crystalline patterns solids arrange themselves in. The entire of the space lattice is built by the repeating arrangement of unit cells. A unit cell is a geometric shape even by itself. It has three edges. And these three edges form three respective angles. The edges of a unit cell are as follows
- A: edges defined by lattice vectors b and c
- B: edges defined by lattice vectors a and c
- C: edges defined by lattice vectors a and b
The interfacial angles of the unit cell are as follows:
- α: the angle between edges b and c
- β: angle between edges a and c
- γ: angle between edges a and b
Primitive Unit Cells
A primitive unit cell only has atoms, molecules or ions at the corners of the lattice. There are no particles located at any other position in a primitive unit cell. So essentially primitive unit cell has only one lattice point.
Please subscribe here to get all future updates on this post/page/category/website


 +919674493673
+919674493673  mailus@wbcsmadeeasy.in
mailus@wbcsmadeeasy.in